Finding Roots of Equations: Bracketing Methods
An elementary observation from the previous method is that in most cases, the function changes signs around the roots of an equation. The bracketing methods rely on the intermediate value theorem.
Intermediate Value Theorem
Statement: Let ![]() be continuous and
be continuous and ![]() . Then,
. Then, ![]() such that
such that ![]() . The same applies if
. The same applies if ![]() .
.
The proof for the intermediate value theorem relies on the assumption of continuity of the function ![]() . Intuitively, because the function
. Intuitively, because the function ![]() is continuous, then for the values of
is continuous, then for the values of ![]() to change from
to change from ![]() to
to ![]() it has to pass by every possible value between
it has to pass by every possible value between ![]() and
and ![]() . The consequence of the theorem is that if the function
. The consequence of the theorem is that if the function ![]() is such that
is such that ![]() , then, there is
, then, there is ![]() such that
such that ![]() . We can proceed to find
. We can proceed to find ![]() iteratively using either the bisection method or the false position method.
iteratively using either the bisection method or the false position method.
Bisection Method
In the bisection method, if ![]() , an estimate for the root of the equation
, an estimate for the root of the equation ![]() can be found as the average of
can be found as the average of ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
![]()
Upon evaluating ![]() , the next iteration would be to set either
, the next iteration would be to set either ![]() or
or ![]() such that for the next iteration the root
such that for the next iteration the root ![]() is between
is between ![]() and
and ![]() . The following describes an algorithm for the bisection method given
. The following describes an algorithm for the bisection method given ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and maximum number of iterations:
, and maximum number of iterations:
Step 1: Evaluate ![]() and
and ![]() to ensure that
to ensure that ![]() . Otherwise, exit with an error.
. Otherwise, exit with an error.
Step 2: Calculate the value of the root in iteration ![]() as
as ![]() . Check which of the following applies:
. Check which of the following applies:
- If
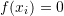 , then the root has been found, the value of the error
, then the root has been found, the value of the error 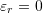 . Exit.
. Exit. - If
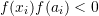 , then for the next iteration,
, then for the next iteration, 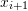 is bracketed between
is bracketed between 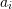 and
and 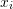 . The value of
. The value of 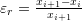 .
. - If
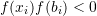 , then for the next iteration,
, then for the next iteration, 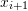 is bracketed between
is bracketed between 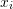 and
and 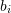 . The value of
. The value of 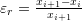 .
.
Step 3: Set ![]() . If
. If ![]() reaches the maximum number of iterations or if
reaches the maximum number of iterations or if ![]() , then the iterations are stopped. Otherwise, return to step 2 with the new interval
, then the iterations are stopped. Otherwise, return to step 2 with the new interval ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Example
Setting ![]() and applying this process to
and applying this process to ![]() with
with ![]() and
and ![]() yields the estimate
yields the estimate ![]() after 9 iterations with
after 9 iterations with ![]() as shown below. Similarly, applying this process to
as shown below. Similarly, applying this process to ![]() with
with ![]() and
and ![]() yields the estimate
yields the estimate ![]() after 10 iterations with
after 10 iterations with ![]() while applying this process to
while applying this process to ![]() with
with ![]() and
and ![]() yields the estimate
yields the estimate ![]() after 9 iterations with
after 9 iterations with ![]() :
:

Clear[f, x, ErrorTable, ei]
f[x_] := Sin[5 x] + Cos[2 x]
(*The following function returns x_i and the new interval (a,b) along with an error note. The order of the output is {xi,new a, new b, note}*)
bisec2[f_, a_, b_] := (xi = (a + b)/2; Which[
f[a]*f[b] > 0, {xi, a, b, "Root Not Bracketed"},
f[xi] == 0, {xi, a, b, "Root Found"},
f[xi]*f[a] < 0, {xi, a, xi, "Root between a and xi"},
f[xi]*f[b] < 0, {xi, xi, b, "Root between xi and b"}])
(*Problem Setup*)
MaxIter = 20;
eps = 0.0005;
(*First root*)
ErrorTable = {1};
ErrorNoteTable = {};
atable = {-0.6};
btable = {-0.5};
xtable = {};
i = 1;
Stopcode = "NoStopping";
While[And[i <= MaxIter, Stopcode == "NoStopping"],
ri = bisec2[f, atable[[i]], btable[[i]]];
If[ri[[4]] == "Root Not Bracketed", xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]];ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]]; Break[]];
If[ri[[4]] == "Root Found", xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]]; ErrorTable = Append[ErrorTable, 0];ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]]; Break[]];
atable = Append[atable, ri[[2]]];
btable = Append[btable, ri[[3]]];
xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]];
ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]];
If[i != 1,
ei = (xtable[[i]] - xtable[[i - 1]])/xtable[[i]];
ErrorTable = Append[ErrorTable, ei]];
If[Abs[ErrorTable[[i]]] > eps, Stopcode = "NoStopping", Stopcode = "Stop"];
i++]
Title = {"Iteration", "a", "b", "x_i", "f[a]", "f[b]", "f[x_i]", "er", "ErrorNote"};
T2 = Table[{i, atable[[i]], btable[[i]], xtable[[i]], f[atable[[i]]], f[btable[[i]]], f[xtable[[i]]], ErrorTable[[i]], ErrorNoteTable[[i]]}, {i, Length[xtable]}];
T2 = Prepend[T2, Title];
T2 // MatrixForm
(*Second Root*)
ErrorTable = {1};
ErrorNoteTable = {};
atable = {-0.3};
btable = {-0.2};
xtable = {};
i = 1;
Stopcode = "NoStopping";
While[And[i <= MaxIter, Stopcode == "NoStopping"],
ri = bisec2[f, atable[[i]], btable[[i]]];
If[ri[[4]] == "Root Not Bracketed", xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]];ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]]; Break[]];
If[ri[[4]] == "Root Found", xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]]; ErrorTable = Append[ErrorTable, 0];ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]]; Break[]];
atable = Append[atable, ri[[2]]];
btable = Append[btable, ri[[3]]];
xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]];
ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]];
If[i != 1,
ei = (xtable[[i]] - xtable[[i - 1]])/xtable[[i]];
ErrorTable = Append[ErrorTable, ei]];
If[Abs[ErrorTable[[i]]] > eps, Stopcode = "NoStopping", Stopcode = "Stop"];
i++]
Title = {"Iteration", "a", "b", "x_i", "f[a]", "f[b]", "f[x_i]", "er", "ErrorNote"};
T2 = Table[{i, atable[[i]], btable[[i]], xtable[[i]], f[atable[[i]]], f[btable[[i]]], f[xtable[[i]]], ErrorTable[[i]], ErrorNoteTable[[i]]}, {i, Length[xtable]}];
T2 = Prepend[T2, Title];
T2 // MatrixForm
(*Third Root*)
ErrorTable = {1};
ErrorNoteTable = {};
atable = {0.6};
btable = {0.7};
xtable = {};
i = 1;
Stopcode = "NoStopping";
While[And[i <= MaxIter, Stopcode == "NoStopping"],
ri = bisec2[f, atable[[i]], btable[[i]]];
If[ri[[4]] == "Root Not Bracketed", xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]];ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]]; Break[]];
If[ri[[4]] == "Root Found", xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]]; ErrorTable = Append[ErrorTable, 0];ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]]; Break[]];
atable = Append[atable, ri[[2]]];
btable = Append[btable, ri[[3]]];
xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]];
ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]];
If[i != 1,
ei = (xtable[[i]] - xtable[[i - 1]])/xtable[[i]];
ErrorTable = Append[ErrorTable, ei]];
If[Abs[ErrorTable[[i]]] > eps, Stopcode = "NoStopping", Stopcode = "Stop"];
i++]
Title = {"Iteration", "a", "b", "x_i", "f[a]", "f[b]", "f[x_i]", "er", "ErrorNote"};
T2 = Table[{i, atable[[i]], btable[[i]], xtable[[i]], f[atable[[i]]], f[btable[[i]]], f[xtable[[i]]], ErrorTable[[i]], ErrorNoteTable[[i]]}, {i, Length[xtable]}];
T2 = Prepend[T2, Title];
T2 // MatrixForm
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
def f(x): return np.sin(5*x) + np.cos(2*x)
def bisec2(f,a,b):
xi = (a + b)/2
if f(a)*f(b) > 0: return [xi, a, b, "Root Not Bracketed"]
elif f(xi) == 0: return [xi, a, b, "Root Found"]
elif f(xi)*f(a) < 0: return [xi, a, xi, "Root between a and xi"]
elif f(xi)*f(b) < 0: return [xi, xi, b, "Root between xi and b"]
def bisection(ErrorTable,ErrorNoteTable,atable,btable,xtable):
MaxIter = 20
eps = 0.0005
Stopcode = "NoStopping"
i = 0
while i <= MaxIter and Stopcode == "NoStopping":
ri = bisec2(f, atable[i], btable[i])
if ri[3] == "Root Not Bracketed":
xtable.append(ri[0])
ErrorNoteTable.append(ri[3])
break
if ri[3] == "Root Found":
xtable.append(ri[0])
ErrorTable.append(0)
ErrorNoteTable.append(ri[3])
break
atable.append(ri[1])
btable.append(ri[2])
xtable.append(ri[0])
ErrorNoteTable.append(ri[3])
if i != 0:
ei = (xtable[i] - xtable[i - 1])/xtable[i]
ErrorTable.append(ei)
if abs(ErrorTable[i]) > eps:
Stopcode = "NoStopping"
else:
Stopcode = "Stop"
i+=1
T2 = ([[i, atable[i], btable[i], xtable[i], f(atable[i]),
f(btable[i]), f(xtable[i]), ErrorTable[i],
ErrorNoteTable[i]] for i in range(len(xtable))])
T2 = pd.DataFrame(T2, columns=["Iteration", "a", "b", "x_i", "f[a]", "f[b]", "f[x_i]", "er", "ErrorNote"])
display(T2)
# First Root
ErrorTable = [1]
ErrorNoteTable = []
atable = [-0.6]
btable = [-0.5]
xtable = []
print("First Root")
bisection(ErrorTable,ErrorNoteTable,atable,btable,xtable)
# Second Root
ErrorTable = [1]
ErrorNoteTable = []
atable = [-0.3]
btable = [-0.2]
xtable = []
print("Second Root")
bisection(ErrorTable,ErrorNoteTable,atable,btable,xtable)
# Third Root
ErrorTable = [1]
ErrorNoteTable = []
atable = [0.6]
btable = [0.7]
xtable = []
print("Third Root")
bisection(ErrorTable,ErrorNoteTable,atable,btable,xtable)
The following code can be used to implement the bisection method in MATLAB. For the sake of demonstration, it finds the roots of the function in above example. The example function is defined in another file
The following tool illustrates this process for ![]() and
and ![]() . Use the slider to view the process after each iteration. In the first iteration, the interval
. Use the slider to view the process after each iteration. In the first iteration, the interval ![]() .
. ![]() , so,
, so, ![]() . In the second iteration, the interval becomes
. In the second iteration, the interval becomes ![]() and the new estimate
and the new estimate ![]() . The relative approximate error in the estimate
. The relative approximate error in the estimate ![]() . You can view the process to see how it converges after 12 iterations.
. You can view the process to see how it converges after 12 iterations.
Error Estimation
If ![]() is the true value of the root and
is the true value of the root and ![]() is the estimate, then, the number of iterations
is the estimate, then, the number of iterations ![]() needed to ensure that the absolute value of the error
needed to ensure that the absolute value of the error ![]() is less than or equal to a certain value can be easily obtained. Let
is less than or equal to a certain value can be easily obtained. Let ![]() be the length of the original interval used. The first estimate
be the length of the original interval used. The first estimate ![]() and so, in the next iteration, the interval where the root is contained has a length of
and so, in the next iteration, the interval where the root is contained has a length of ![]() . As the process evolves, the interval for the iteration number
. As the process evolves, the interval for the iteration number ![]() has a length of
has a length of ![]() . Since the true value exists in an interval of length
. Since the true value exists in an interval of length ![]() , the absolute value of the error is such that:
, the absolute value of the error is such that:
![]()
Therefore, for a desired estimate of the absolute value of the error, say ![]() , the number of iterations required is:
, the number of iterations required is:
![]()
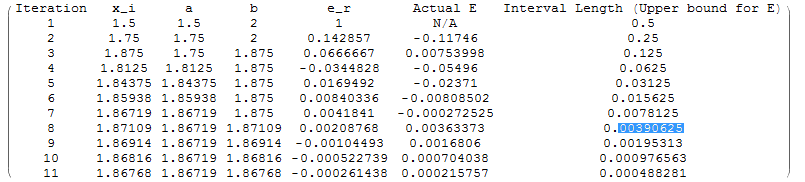
Example
As an example, consider ![]() , if we wish to find the root of the equation
, if we wish to find the root of the equation ![]() in the interval
in the interval ![]() with an absolute error less than or equal to 0.004, the number of iterations required is 8:
with an absolute error less than or equal to 0.004, the number of iterations required is 8:
![]()
The actual root with 10 significant digits is ![]() .
.
Using the process above, after the first iteration, ![]() and so, the root lies between
and so, the root lies between ![]() and
and ![]() . So, the length of the interval is equal to 0.5 and the error in the estimate is less than 0.5. The length of the interval after iteration 8 is equal to 0.0039 and so the error in the estimate is less than 0.0039. It should be noted however that the actual error was less than this upper bound after the seventh iteration.
. So, the length of the interval is equal to 0.5 and the error in the estimate is less than 0.5. The length of the interval after iteration 8 is equal to 0.0039 and so the error in the estimate is less than 0.0039. It should be noted however that the actual error was less than this upper bound after the seventh iteration.
Clear[f, x, tt, ErrorTable, nn];
f[x_] := x^3 + x^2 - 10;
bisec[f_, a_, b_] := (xi = (a + b)/2;
Which[f[a]*f[b] > 0, {xi, a, b, "Root Not Bracketed"},
f[xi] == 0, {xi, a, b, "Root Found"},
f[xi]*f[a] < 0, {xi, a, xi, "Root between a and xi"},
f[xi]*f[b] < 0, {xi, xi, b, "Root between xi and b"}]);
(*Exact Solution*)
t = Solve[x^3 + x^2 - 10 == 0, x]
Vt = N[x /. t[[1]], 10]
(*Problem Setup*)
MaxIter = 20;
eps = 0.0005;
(*First root*)
x = {bisec[f, 1., 2]};
ErrorTable = {1};
ErrorTable2 = {"N/A"};
IntervalLength = {0.5};
i = 2;
While[And[i <= MaxIter, Abs[ErrorTable[[i - 1]]] > eps],
ri = bisec[f, x[[i - 1, 2]], x[[i - 1, 3]]];
If[ri == "Error, root is not bracketed",
ErrorTable[[1]] = "Error, root is not bracketed"; Break[]];
x = Append[x, ri]; ei = (x[[i, 1]] - x[[i - 1, 1]])/x[[i, 1]];
e2i = x[[i, 1]] - Vt; ErrorTable = Append[ErrorTable, ei];
IntervalLength =
Append[IntervalLength, (x[[i - 1, 3]] - x[[i - 1, 2]])/2];
ErrorTable2 = Append[ErrorTable2, e2i]; i++]
x // MatrixForm
ErrorTable // MatrixForm
Title = {"Iteration", "x_i", "a", "b", "e_r", "Actual E",
"Interval Length (Upper bound for E)"};
T2 = Table[{i, x[[i, 1]], x[[i, 2]], x[[i, 3]], ErrorTable[[i]],
ErrorTable2[[i]], IntervalLength[[i]]}, {i, 1, Length[x]}];
T2 = Prepend[T2, Title];
T2 // MatrixForm
import sympy as sp
import pandas as pd
def f(x): return x**3 + x**2 - 10
def bisec(f,a,b):
xi = (a + b)/2
if f(a)*f(b) > 0: return [xi, a, b, "Root Not Bracketed"]
elif f(xi) == 0: return [xi, a, b, "Root Found"]
elif f(xi)*f(a) < 0: return [xi, a, xi, "Root between a and xi"]
elif f(xi)*f(b) < 0: return [xi, xi, b, "Root between xi and b"]
# Exact Solution
x = sp.symbols('x')
t = list(sp.nonlinsolve([x**3 + x**2 - 10], [x]))
Vt = sp.N(t[0][0])
print("Vt:",Vt)
# Problem Setup
MaxIter = 20
eps = 0.0005
# First Root
x = [bisec(f, 1., 2)]
ErrorTable = [1]
ErrorTable2 = ["N/A"]
IntervalLength = [0.5]
i = 1
while i <= MaxIter and abs(ErrorTable[i - 1]) > eps:
ri = bisec(f, x[i - 1][1], x[i - 1][2])
if ri=="Error, root is not bracketed":
ErrorTable[0]="Error, root is not bracketed"
break
x.append(ri)
ei = (x[i][0] - x[i - 1][0])/x[i][0]
e2i = x[i][0] - Vt
ErrorTable.append(ei)
IntervalLength.append((x[i - 1][2] - x[i - 1][1])/2)
ErrorTable2.append(e2i)
i+=1
print("x Table");
display(pd.DataFrame(x))
print("ErrorTable")
display(pd.DataFrame(ErrorTable))
T2 = ([[i, x[i][0], x[i][1], x[i][2], ErrorTable[i], ErrorTable2[i],
IntervalLength[i]] for i in range(len(x))])
pd.DataFrame(T2, columns=["Iteration", "x_i", "a", "b", "e_r", "Actual E", "Interval Length (Upper bound for E)"])
The procedure for solving the above example in MATLAB is available in the following files. The polynomial function is defined in a separate file.
False Position Method
In the false position method, the new estimate ![]() at iteration
at iteration ![]() is obtained by considering the linear function passing through the two points
is obtained by considering the linear function passing through the two points ![]() and
and ![]() . The point of intersection of this line with the
. The point of intersection of this line with the ![]() axis can be obtained using one of the following formulas:
axis can be obtained using one of the following formulas:
![]()
Upon evaluating ![]() , the next iteration would be to set either
, the next iteration would be to set either ![]() or
or ![]() such that for the next iteration the root
such that for the next iteration the root ![]() is between
is between ![]() and
and ![]() . The following describes an algorithm for the false position method method given
. The following describes an algorithm for the false position method method given ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and maximum number of iterations:
, and maximum number of iterations:
Step 1: Evaluate ![]() and
and ![]() to ensure that
to ensure that ![]() . Otherwise exit with an error.
. Otherwise exit with an error.
Step 2: Calculate the value of the root in iteration ![]() as
as ![]() . Check which of the following applies:
. Check which of the following applies:
- If
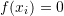 , then the root has been found, the value of the error
, then the root has been found, the value of the error 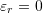 . Exit.
. Exit. - If
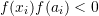 , then for the next iteration,
, then for the next iteration, 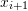 is bracketed between
is bracketed between 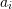 and
and 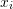 . The value of
. The value of 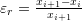 .
. - If
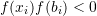 , then for the next iteration,
, then for the next iteration, 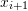 is bracketed between
is bracketed between 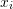 and
and 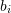 . The value of
. The value of 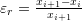 .
.
Step 3: If ![]() reaches the maximum number of iterations or if
reaches the maximum number of iterations or if ![]() , then the iterations are stopped. Otherwise, return to step 2.
, then the iterations are stopped. Otherwise, return to step 2.
Example
Setting ![]() and applying this process to
and applying this process to ![]() with
with ![]() and
and ![]() yields the estimate
yields the estimate ![]() after 3 iterations with
after 3 iterations with ![]() as shown below. Similarly, applying this process to
as shown below. Similarly, applying this process to ![]() with
with ![]() and
and ![]() yields the estimate
yields the estimate ![]() after 4 iterations with
after 4 iterations with ![]() while applying this process to
while applying this process to ![]() with
with ![]() and
and ![]() yields the estimate
yields the estimate ![]() after 3 iterations with
after 3 iterations with ![]() :
:
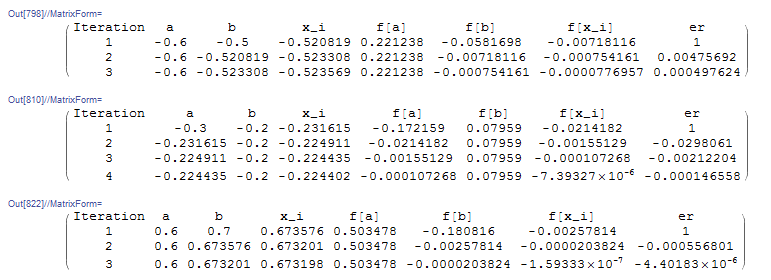
Clear[f, x, ErrorTable, ei]
f[x_] := Sin[5 x] + Cos[2 x]
(*The following function returns x_i and the new interval (a,b) along with an error note. The order of the output is {xi,new a, new b, note}*)
falseposition[f_, a_, b_] := (xi = (a*f[b]-b*f[a])/(f[b]-f[a]); Which[
f[a]*f[b] > 0, {xi, a, b, "Root Not Bracketed"},
f[xi] == 0, {xi, a, b, "Root Found"},
f[xi]*f[a] < 0, {xi, a, xi, "Root between a and xi"},
f[xi]*f[b] < 0, {xi, xi, b, "Root between xi and b"}])
(*Problem Setup*)
MaxIter = 20;
eps = 0.0005;
(*First root*)
ErrorTable = {1};
ErrorNoteTable = {};
atable = {-0.6};
btable = {-0.5};
xtable = {};
i = 1;
Stopcode = "NoStopping";
While[And[i <= MaxIter, Stopcode == "NoStopping"],
ri = falseposition[f, atable[[i]], btable[[i]]];
If[ri[[4]] == "Root Not Bracketed", xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]];ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]]; Break[]];
If[ri[[4]] == "Root Found", xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]]; ErrorTable = Append[ErrorTable, 0];ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]]; Break[]];
atable = Append[atable, ri[[2]]];
btable = Append[btable, ri[[3]]];
xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]];
ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]];
If[i != 1,
ei = (xtable[[i]] - xtable[[i - 1]])/xtable[[i]];
ErrorTable = Append[ErrorTable, ei]];
If[Abs[ErrorTable[[i]]] > eps, Stopcode = "NoStopping", Stopcode = "Stop"];
i++]
Title = {"Iteration", "a", "b", "x_i", "f[a]", "f[b]", "f[x_i]", "er", "ErrorNote"};
T2 = Table[{i, atable[[i]], btable[[i]], xtable[[i]], f[atable[[i]]], f[btable[[i]]], f[xtable[[i]]], ErrorTable[[i]], ErrorNoteTable[[i]]}, {i, Length[xtable]}];
T2 = Prepend[T2, Title];
T2 // MatrixForm
(*Second Root*)
ErrorTable = {1};
ErrorNoteTable = {};
atable = {-0.3};
btable = {-0.2};
xtable = {};
i = 1;
Stopcode = "NoStopping";
While[And[i <= MaxIter, Stopcode == "NoStopping"],
ri = falseposition[f, atable[[i]], btable[[i]]];
If[ri[[4]] == "Root Not Bracketed", xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]];ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]]; Break[]];
If[ri[[4]] == "Root Found", xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]]; ErrorTable = Append[ErrorTable, 0];ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]]; Break[]];
atable = Append[atable, ri[[2]]];
btable = Append[btable, ri[[3]]];
xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]];
ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]];
If[i != 1,
ei = (xtable[[i]] - xtable[[i - 1]])/xtable[[i]];
ErrorTable = Append[ErrorTable, ei]];
If[Abs[ErrorTable[[i]]] > eps, Stopcode = "NoStopping", Stopcode = "Stop"];
i++]
Title = {"Iteration", "a", "b", "x_i", "f[a]", "f[b]", "f[x_i]", "er", "ErrorNote"};
T2 = Table[{i, atable[[i]], btable[[i]], xtable[[i]], f[atable[[i]]], f[btable[[i]]], f[xtable[[i]]], ErrorTable[[i]], ErrorNoteTable[[i]]}, {i, Length[xtable]}];
T2 = Prepend[T2, Title];
T2 // MatrixForm
(*Third Root*)
ErrorTable = {1};
ErrorNoteTable = {};
atable = {0.6};
btable = {0.7};
xtable = {};
i = 1;
Stopcode = "NoStopping";
While[And[i <= MaxIter, Stopcode == "NoStopping"],
ri = falseposition[f, atable[[i]], btable[[i]]];
If[ri[[4]] == "Root Not Bracketed", xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]];ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]]; Break[]];
If[ri[[4]] == "Root Found", xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]]; ErrorTable = Append[ErrorTable, 0];ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]]; Break[]];
atable = Append[atable, ri[[2]]];
btable = Append[btable, ri[[3]]];
xtable = Append[xtable, ri[[1]]];
ErrorNoteTable = Append[ErrorNoteTable, ri[[4]]];
If[i != 1,
ei = (xtable[[i]] - xtable[[i - 1]])/xtable[[i]];
ErrorTable = Append[ErrorTable, ei]];
If[Abs[ErrorTable[[i]]] > eps, Stopcode = "NoStopping", Stopcode = "Stop"];
i++]
Title = {"Iteration", "a", "b", "x_i", "f[a]", "f[b]", "f[x_i]", "er", "ErrorNote"};
T2 = Table[{i, atable[[i]], btable[[i]], xtable[[i]], f[atable[[i]]], f[btable[[i]]], f[xtable[[i]]], ErrorTable[[i]], ErrorNoteTable[[i]]}, {i, Length[xtable]}];
T2 = Prepend[T2, Title];
T2 // MatrixForm
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
def f(x): return np.sin(5*x) + np.cos(2*x)
# The following function returns x_i and the new interval (a,b) along with an error note. The order of the output is {xi,new a, new b, note}
def falseposition(f,a,b):
xi = (a*f(b)-b*f(a))/(f(b)-f(a))
if f(a)*f(b) > 0: return [xi, a, b, "Root Not Bracketed"]
elif f(xi) == 0: return [xi, a, b, "Root Found"]
elif f(xi)*f(a) < 0: return [xi, a, xi, "Root between a and xi"]
elif f(xi)*f(b) < 0: return [xi, xi, b, "Root between xi and b"]
def falseposition2(ErrorTable,ErrorNoteTable,atable,btable,xtable):
MaxIter = 20
eps = 0.0005
Stopcode = "NoStopping"
i = 0
while i <= MaxIter and Stopcode == "NoStopping":
ri = falseposition(f, atable[i], btable[i])
if ri[3] == "Root Not Bracketed":
xtable.append(ri[0])
ErrorNoteTable.append(ri[3])
break
if ri[3] == "Root Found":
xtable.append(ri[0])
ErrorTable.append(0)
ErrorNoteTable.append(ri[3])
break
atable.append(ri[1])
btable.append(ri[2])
xtable.append(ri[0])
ErrorNoteTable.append(ri[3])
if i != 0:
ei = (xtable[i] - xtable[i - 1])/xtable[i]
ErrorTable.append(ei)
if abs(ErrorTable[i]) > eps:
Stopcode = "NoStopping"
else:
Stopcode = "Stop"
i+=1
T2 = ([[i, atable[i], btable[i], xtable[i], f(atable[i]),
f(btable[i]), f(xtable[i]), ErrorTable[i],
ErrorNoteTable[i]] for i in range(len(xtable))])
T2 = pd.DataFrame(T2, columns=["Iteration", "a", "b", "x_i", "f[a]", "f[b]", "f[x_i]", "er", "ErrorNote"])
display(T2)
# First Root
ErrorTable = [1]
ErrorNoteTable = []
atable = [-0.6]
btable = [-0.5]
xtable = []
print("First Root")
falseposition2(ErrorTable,ErrorNoteTable,atable,btable,xtable)
# Second Root
ErrorTable = [1]
ErrorNoteTable = []
atable = [-0.3]
btable = [-0.2]
xtable = []
print("Second Root")
falseposition2(ErrorTable,ErrorNoteTable,atable,btable,xtable)
# Third Root
ErrorTable = [1]
ErrorNoteTable = []
atable = [0.6]
btable = [0.7]
xtable = []
print("Third Root")
falseposition2(ErrorTable,ErrorNoteTable,atable,btable,xtable)
The procedure for implementing the false position root finding algorithm in MATLAB is available in the following files. The example function is defined in a separate file.
The following tool illustrates this process for ![]() and
and ![]() . Use the slider to view the process after each iteration. In the first iteration, the interval
. Use the slider to view the process after each iteration. In the first iteration, the interval ![]() .
. ![]() , so,
, so, ![]() . In the second iteration, the interval becomes
. In the second iteration, the interval becomes ![]() and the new estimate
and the new estimate ![]() . The relative approximate error in the estimate
. The relative approximate error in the estimate ![]() . You can view the process to see how it converges after very few iterations.
. You can view the process to see how it converges after very few iterations.

Thank you so much for this content, this is very helpful, and will be passing this along to my classmates. I wish I could’ve found this earlier.
Thank you
Hi, very good internet textbook! A suggestion: for easy citation, you could have the formatted bibtex and plain text entries for each page, this could be generated automatically. It would make it easier to cite your good work. Of course, as I am referring to this page, I did the formatting as requested at the bottom of the page to cite your work appropriately.